FIBROID AND FERTILITY
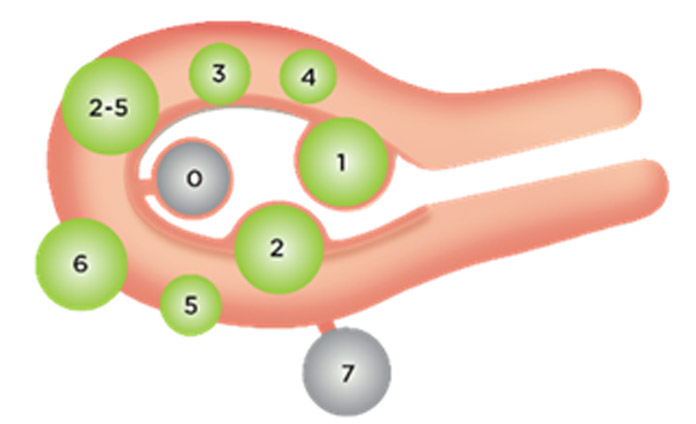
- It is well accepted that Type 0,1,2 fibroids reduce fertility and increase miscarriage. Hence removal of such fibroids by Transcervical Resection of Myoma is advised.
- Type 6,7 fibroids do not usually affect fertility, unless they are very large and distorting the pelvic anatomy. Hence such fibroids can be left alone if they are not >6cm.
- For large Type 3,4,5 fibroids, studies have shown a 21% reduction in pregnancy rates and a 24% increase in miscarriage rates.
(Sunkara 2010)
PREGNANCY WITH FIBROID
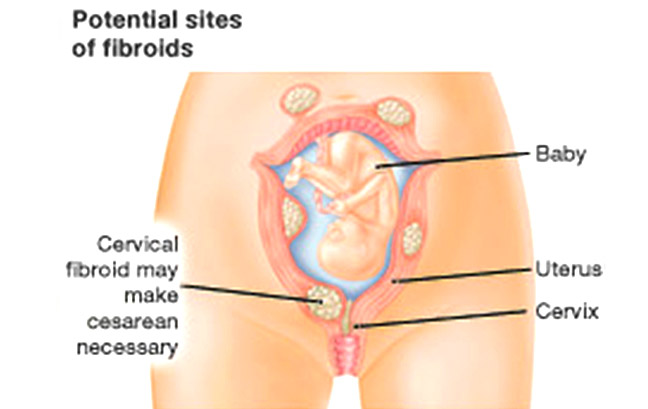
Most women with fibroids go through pregnancy without problems. A few women may find their fibroids grow in pregnancy to cause pain from a condition called red degeneration. Some fibroids may prevent a vaginal delivery, so a caesarian section is needed. After delivery, most fibroids will shrink and return to their original size.
A few women with fibroids > 5cm may have problems in pregnancy like
- miscarriage (1.2x more)
- bleeding in second / third trimester
- premature birth (1.5x more)
- premature placenta separation (3.2x more)
- stillbirth (1.7% more)
FIBROID SURGERY AND PREGNANCY

When fibroid surgery is done prior to getting pregnant, two issues need to be addressed.
- The duration between surgery and future pregnancy
- The risk of the fibroid surgery area tearing in pregnancy, called uterine rupture.
How long to wait
After fibroid surgery, it is advisable to wait at least 6 months before trying to get pregnant. One small study using MRI to assess the healing process after fibroid surgery, found that healing is satisfactory in 70% of cases at 3 months, 80% at 6 months and 95% at 12 months.
(Tsuji 2006)
Uterine rupture
This is the most serious complication to occur in pregnancy after fibroid surgery. Fortunately, the risk is very low, at 0.75%. It can happen in the early third trimester before labour, with significant risk to the baby. For women going into labour after fibroid surgery, there is >85% chance of a normal vaginal delivery with no uterine rupture.
(Claeys 2014)


 Top
Top